© Science Actualités/CSI CNRS Audiovisuel 1996
Reference
233
Fragmented body (The)
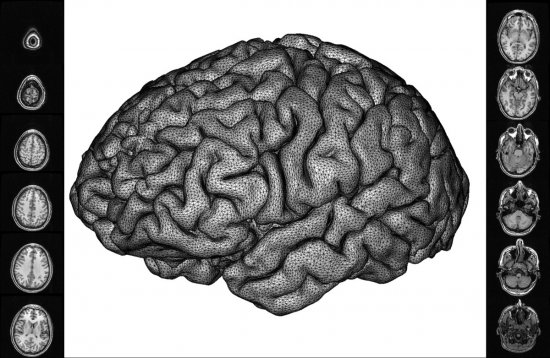
The new imaging equipments for medical diagnosis, which can show the depths of the human body are described in their use in hospitals by physicians and scientists in various fields.
The Orsay hospital, thanks to a cyclotron, can produce radioactive elements, which, fastened to biological molecules, are detected by a positron camera, which can follow the motions of these tracers in the human body. At Institut Curie, the radioactive molecules injected in the body are tracked by a gamma camera. Gammagraphy is used to detect bone anomalies but do not allow an accurate diagnosis.
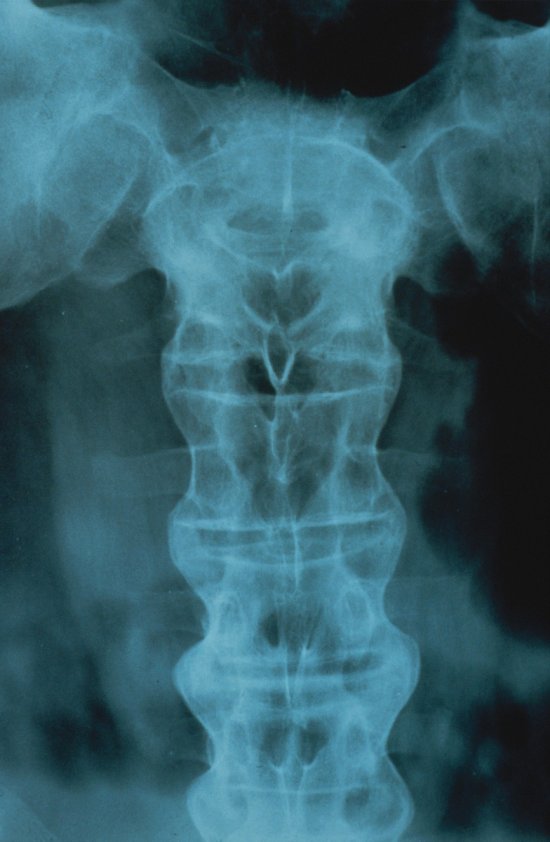
With X-ray scanner, a combination of X-ray radiography with computerized image processing, cross-section images of an organ are obtained.
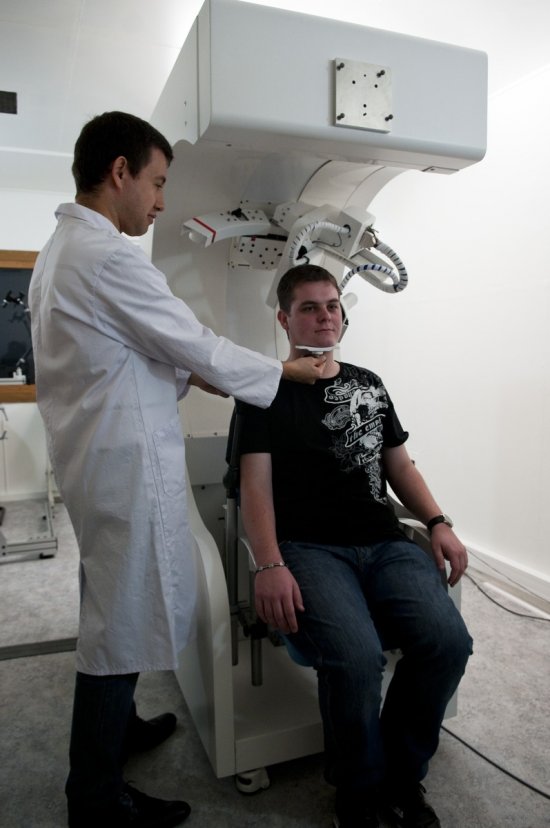
The Val de Grâce hospital use magnetic resonance imaging for delicate operations, for example brain surgery.
Each technique has its advantages and can improve medical diagnosis.
Duration
Production year
Définition
Color
Sound
Version(s)
Original material
The use of media visible on the CNRS Images Platform can be granted on request. Any reproduction or representation is forbidden without prior authorization from CNRS Images (except for resources under Creative Commons license).
No modification of an image may be made without the prior consent of CNRS Images.
No use of an image for advertising purposes or distribution to a third party may be made without the prior agreement of CNRS Images.
For more information, please consult our general conditions