© Kimberly REBET / Gabriel KROUK / BPMP / CNRS Images
Reference
20170091_0001
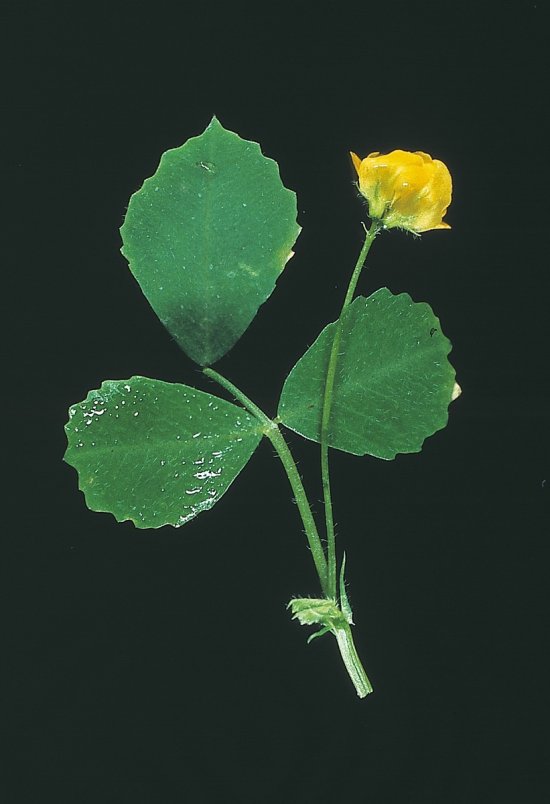
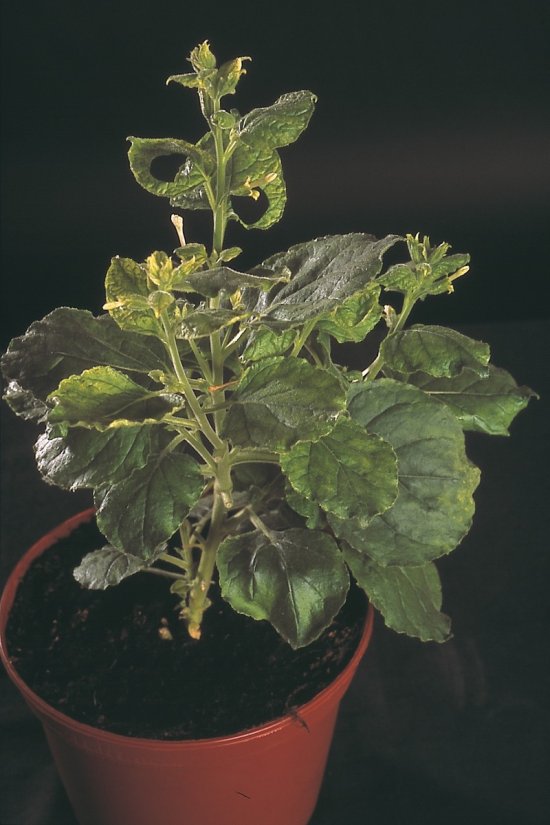
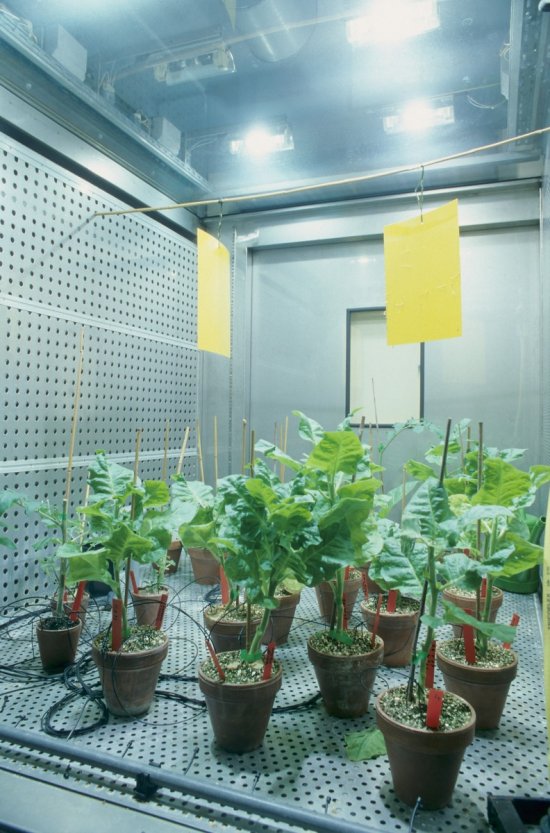
Mutants nains d'arabette des dames issus de la technique CRISPR-Cas9
CRISPR-Cas9 is an innovative molecular scissors technique that can be used to modify the genome in a targeted way. Here, it has been used to delete the BRI1 gene of Arabidopsis thaliana, which is involved in the perception of a plant growth regulator. Among the non-mutant plants of normal size can be seen mutant plants recognizable due to their small size and bud-like appearance. The acronym CRISPR, Clustered Regularly Interspaced Short Palindromic Repeats, refers to a set of similar sequences present in the DNA of a bacteria. These are interspersed with foreign sequences, such as viral DNA, integrated into the DNA of the bacterium by certain proteins when the virus entered, in order to memorise these sequences. By combining these sequences transcribed into RNA with an endonuclease, the Cas9 protein, RNA recognition can be used to cut the DNA of the virus when it enters the bacterium again. By including the known DNA between these CRISPR sequences, in the place of the viral DNA, it is then possible to cut a specific point in the plant genome, such as, in this case, the middle of the sequence that encodes the BRI1 protein, altering its expression. Although other specific genome modification techniques already exist, CRISPR-Cas9 is of interest due to its ease of design and its effectiveness in all types of cells. In order to test this new technique, research scientists have deleted the BRI1 gene, causing a mutation that is known to produce dwarf plants in Arabidopsis thaliana. This choice of mutation enables them to see with the naked eye whether the mutation has been successful.
The use of media visible on the CNRS Images Platform can be granted on request. Any reproduction or representation is forbidden without prior authorization from CNRS Images (except for resources under Creative Commons license).
No modification of an image may be made without the prior consent of CNRS Images.
No use of an image for advertising purposes or distribution to a third party may be made without the prior agreement of CNRS Images.
For more information, please consult our general conditions