© Violette DA CUNHA / Philippe GLASER / Pierre LECHAT / Erika SOUCHE / Ivan MOSZER / IPL / C3BI / CNRS Images
Reference
20170074_0013
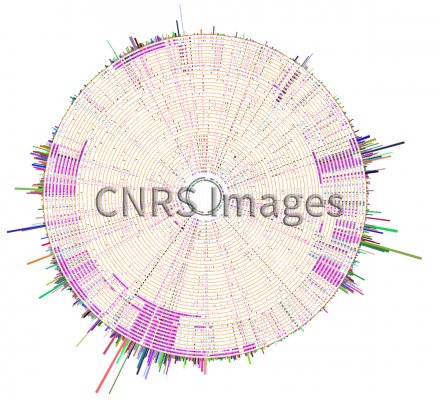
Représentation circulaire de la distribution et de la recombinaison de SNPs
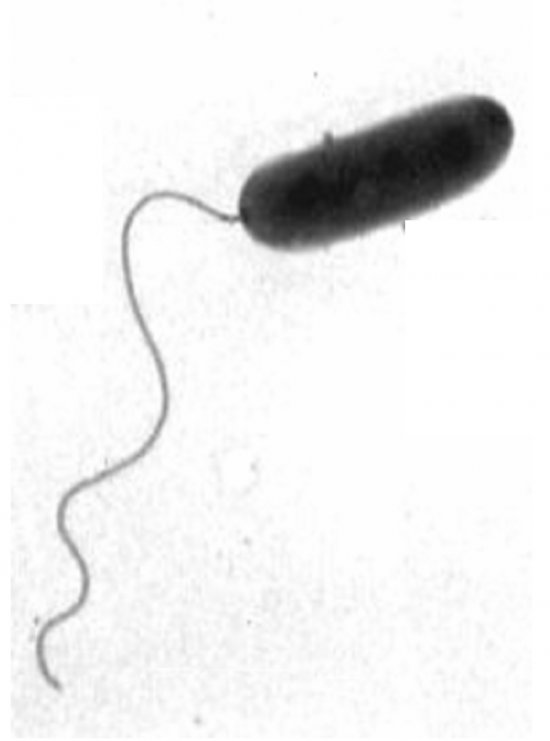
Circular representation of the distribution and recombination of SNPs (minor variations in the genome within a population or species that cause morphological differences or a predisposition to certain diseases). Here, research scientists have compared lines of the cc1 clonotype of group B Streptococcus agalactiae (GBS) to the Streptococcus agalactiae bacterium line, which is a major cause of neonatal bacterial infections. The recent development of new sequencing technologies means these organisms can be studied at the level of the genome. In the case of Streptococcus, this study made it possible to reconstruct the recent evolutionary history of the major clones responsible for infections. Intergenic mutations are shown in black, synonymous mutations in pink and nonsynonymous mutations in blue. The recombination regions are the areas most densely populated by SNPs. This image was generated using the SynTView software package (Lechat P, Souche E, Moszer I).
The use of media visible on the CNRS Images Platform can be granted on request. Any reproduction or representation is forbidden without prior authorization from CNRS Images (except for resources under Creative Commons license).
No modification of an image may be made without the prior consent of CNRS Images.
No use of an image for advertising purposes or distribution to a third party may be made without the prior agreement of CNRS Images.
For more information, please consult our general conditions