Production year
2013
© Jean-Claude MOSCHETTI / ISCR / CNRS Images
20130001_2172
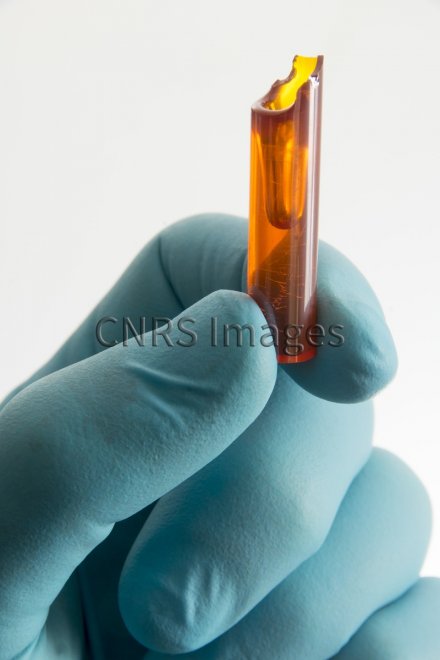
Ce matériau est un verre de chalcogénure dopé avec une terre rare, le néodyme. Il est composé de soufre, d'antimoine, de gallium et de germanium. Il possède la propriété de transmettre la lumière dans l'infrarouge jusqu'à 12 µm. Ce verre est étiré sous forme de fibres optiques, afin d'en faire des capteurs ou des sources pour la détection d'espèces chimiques dans l'infrarouge.
The use of media visible on the CNRS Images Platform can be granted on request. Any reproduction or representation is forbidden without prior authorization from CNRS Images (except for resources under Creative Commons license).
No modification of an image may be made without the prior consent of CNRS Images.
No use of an image for advertising purposes or distribution to a third party may be made without the prior agreement of CNRS Images.
For more information, please consult our general conditions
2013
Our work is guided by the way scientists question the world around them and we translate their research into images to help people to understand the world better and to awaken their curiosity and wonderment.