Production year
2007
© Claude SAUTER/IBMC/CNRS Images
20140001_1092
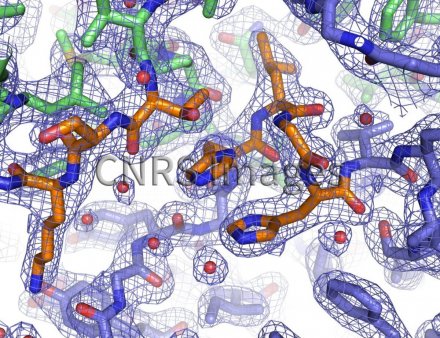
Image 3D d'une protéine obtenue par cristallographie des rayons X. Le signal de diffraction des RX émis par le cristal de protéine permet de reconstituer le volume du nuage électronique (volume bleu) qui entoure les atomes. Le modèle atomique est construit en plaçant les acides aminés au sein de cette carte de densité électronique. La protéine cristallisée est une enzyme, c'est-à-dire un biocatalyseur qui réalise une réaction chimique. Cette image 3D permet de comprendre comment l'enzyme sélectionne et fixe ses molécules cibles et comment elle réalise cette réaction.
The use of media visible on the CNRS Images Platform can be granted on request. Any reproduction or representation is forbidden without prior authorization from CNRS Images (except for resources under Creative Commons license).
No modification of an image may be made without the prior consent of CNRS Images.
No use of an image for advertising purposes or distribution to a third party may be made without the prior agreement of CNRS Images.
For more information, please consult our general conditions
2007
Our work is guided by the way scientists question the world around them and we translate their research into images to help people to understand the world better and to awaken their curiosity and wonderment.