© Jean-Luc DUPONT/INCI/CNRS Images
Reference
20160086_0002
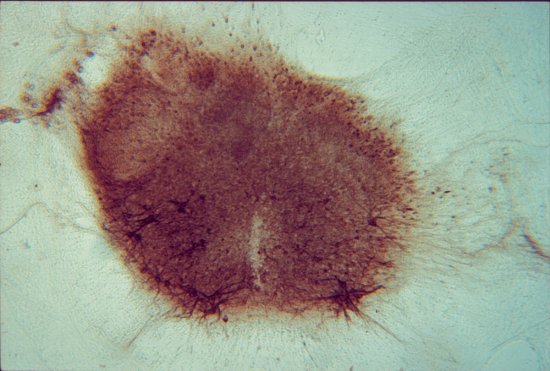
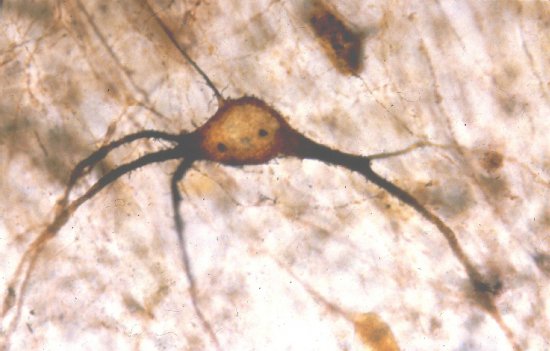
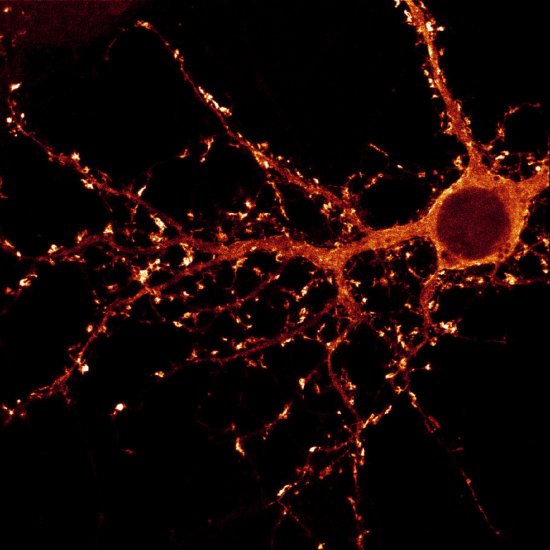
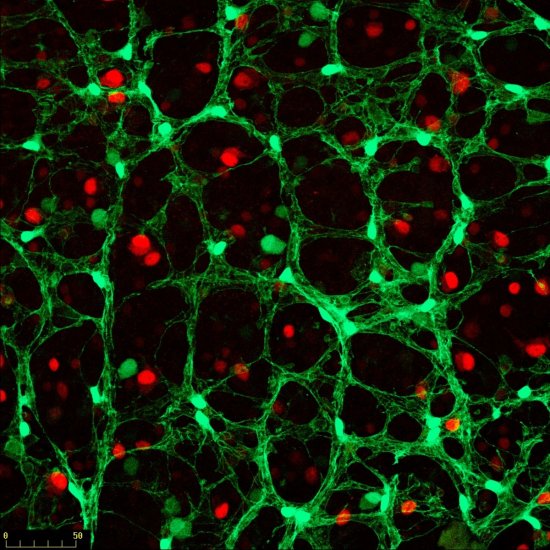
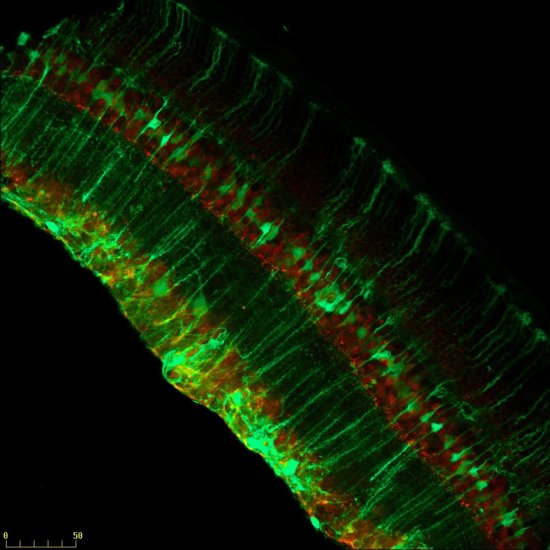
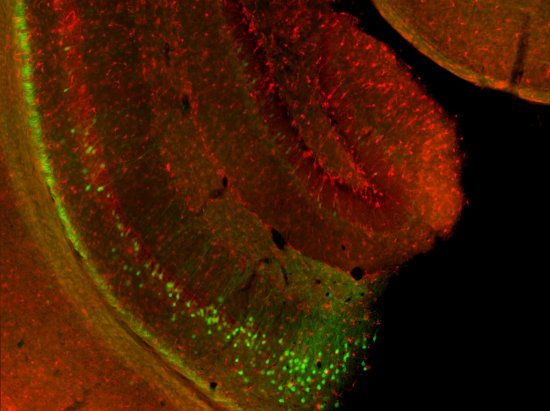
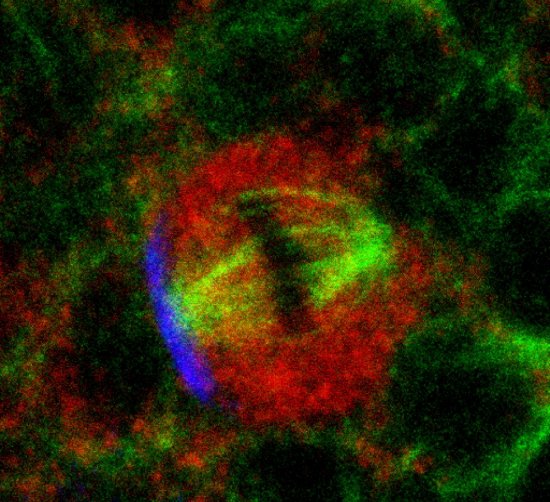
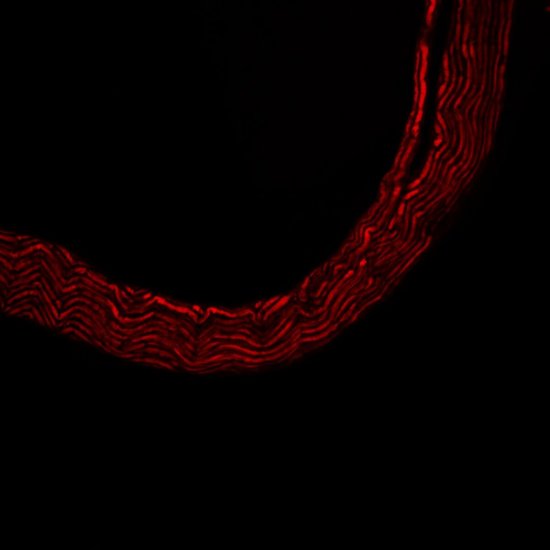
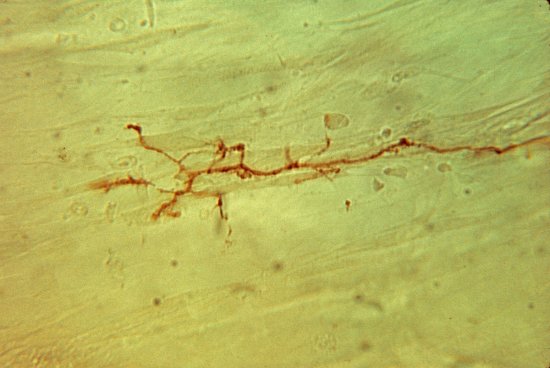
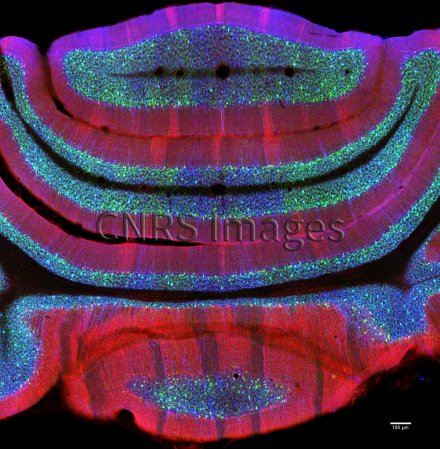
Section of cerebellar cortex, a nerve tissue situated in the cerebellum, in a mouse
Confocal microscopy view of a section of cerebellar cortex, a nerve tissue situated in the cerebellum, in a mouse. The scale bar corresponds to 100 µm. Purkinje cells are marked in red, the Glyt2 type Golgi cells in green and neurogranin type Golgi cells in blue. The cerebellum plays a major role in the control of posture, balance, voluntary mobility and certain cognitive functions. A lot of sensory information arrives in the cerebellar cortex: some of this information is transmitted directly to the Purkinje cells and another part goes to granule cells that are anatomically linked to several thousand Purkinje cells. Researchers have developed a functional map of the synaptic connections between the granule cells and other cell types. They have demonstrated a functional organisation of the neural networks shared across animal species, but which can be modified at any time as required. These networks allow distant zones of the cerebellar cortex to communicate among themselves and to associate with each other dynamically. This work will help to explain how the cerebellum processes and combines information essential to the coordination of motor functions.
The use of media visible on the CNRS Images Platform can be granted on request. Any reproduction or representation is forbidden without prior authorization from CNRS Images (except for resources under Creative Commons license).
No modification of an image may be made without the prior consent of CNRS Images.
No use of an image for advertising purposes or distribution to a third party may be made without the prior agreement of CNRS Images.
For more information, please consult our general conditions