Production year
2015
© Fabien ALCARAZ / INCIA / CNRS Images
20150002_0001
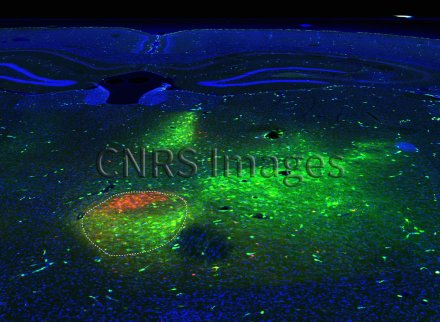
Voies nerveuses marquées en rouge et vert dans deux régions du cortex orbitofrontal d'un rat. Les molécules marquées migrent ensuite pour s'accumuler dans les neurones thalamiques. Un marquage dense des deux traceurs est visible au niveau du thalamus submédian (délimité par des pointillés). Grâce à cette technique de marquage, les chercheurs ont mis en évidence le rôle capital du thalamus submédian dans la prise de décision face à un changement de l'environnement chez le rat. Ce résultat suggère une contribution du thalamus qui pourrait nous permettre d'améliorer notre compréhension de nombreuses pathologies comme la schizophrénie ou encore l'addiction.
The use of media visible on the CNRS Images Platform can be granted on request. Any reproduction or representation is forbidden without prior authorization from CNRS Images (except for resources under Creative Commons license).
No modification of an image may be made without the prior consent of CNRS Images.
No use of an image for advertising purposes or distribution to a third party may be made without the prior agreement of CNRS Images.
For more information, please consult our general conditions
2015
Our work is guided by the way scientists question the world around them and we translate their research into images to help people to understand the world better and to awaken their curiosity and wonderment.