Production year
2011
© François CAILLAUD/SAGASCIENCE/CNRS Images
20110001_0353
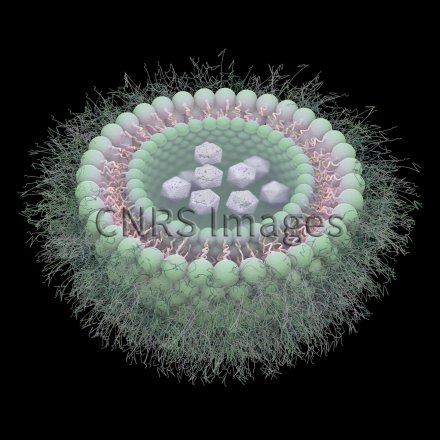
Liposome pégylé dont la surface est recouverte d'un polymère hydrophile et flexible, ici du polyéthylène glycol (PEG). C'est un vecteur de médicament de deuxième génération qui n'est pas capté par le foie comme le sont les vecteurs de première génération. Le liposome est une vésicule biodégradable constituée d'une double couche de phospholipides et d'un compartiment aqueux. Le principe actif du médicament est encapsulé dans la phase aqueuse quand il est hydrophile, et dans la bicouche quand il est lipophile. La structure phospholipidique du liposome est proche de celle de la membrane de la cellule : on dit qu'il est biomimétique. Un liposome est environ 70 fois plus petit qu'un globule rouge. Sa taille varie entre 100 et 300 nm.
The use of media visible on the CNRS Images Platform can be granted on request. Any reproduction or representation is forbidden without prior authorization from CNRS Images (except for resources under Creative Commons license).
No modification of an image may be made without the prior consent of CNRS Images.
No use of an image for advertising purposes or distribution to a third party may be made without the prior agreement of CNRS Images.
For more information, please consult our general conditions
2011
Our work is guided by the way scientists question the world around them and we translate their research into images to help people to understand the world better and to awaken their curiosity and wonderment.