© Laurent GUERIN/CNRS Images
Reference
20050001_0267
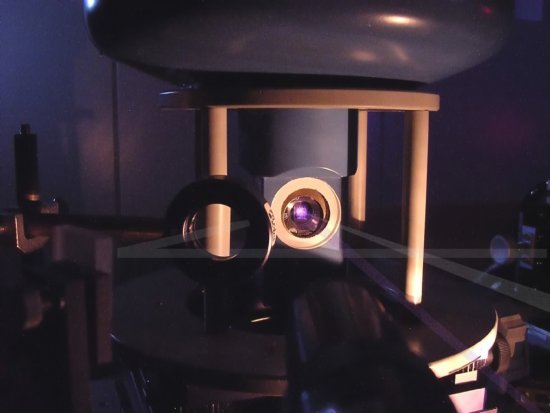
Le cristal moléculaire (au centre) dans son cryostat (appareil utilisé pour le maintenir à basse tem
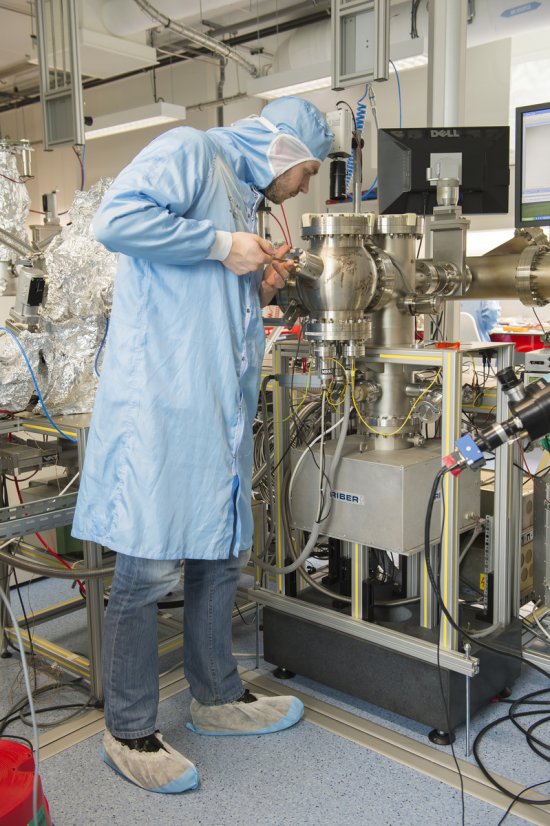
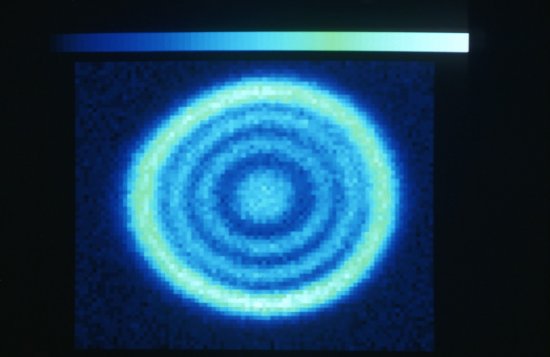
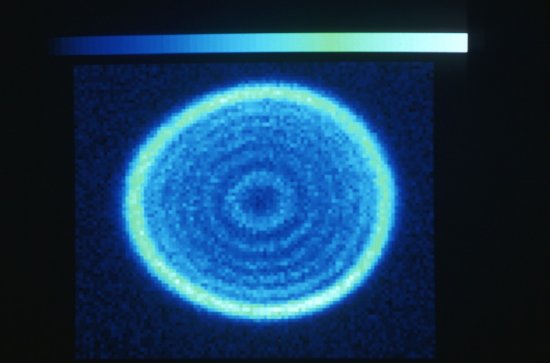
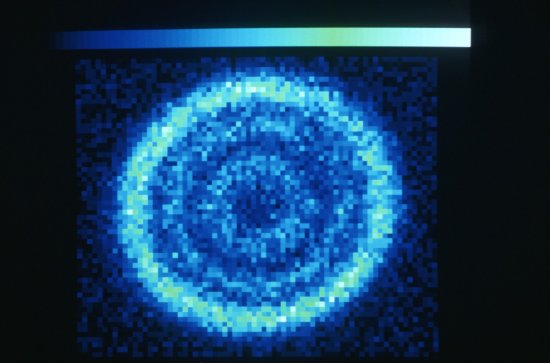
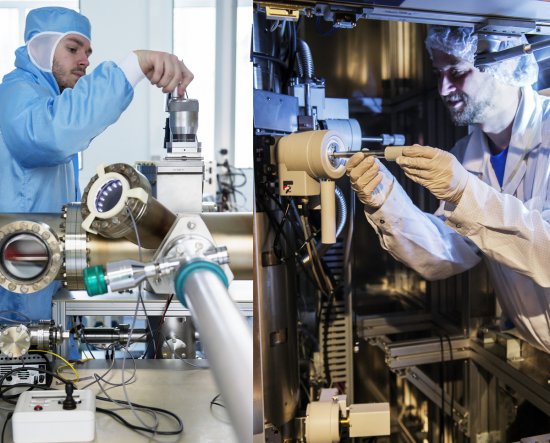
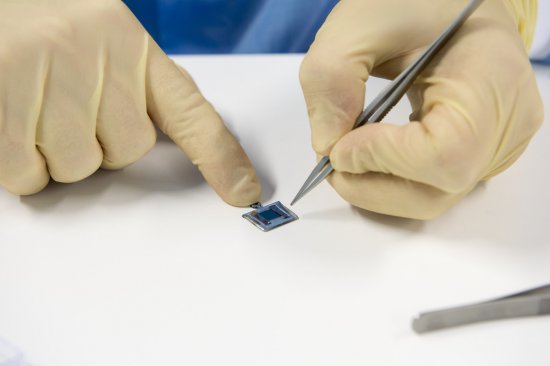
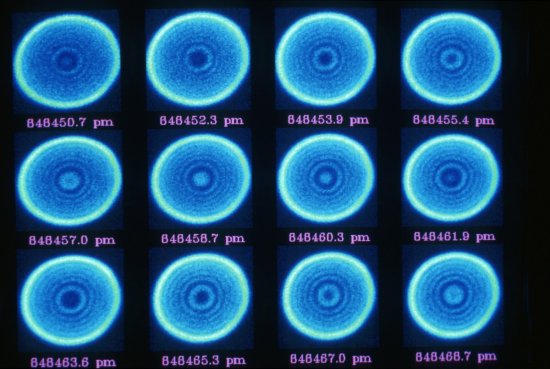
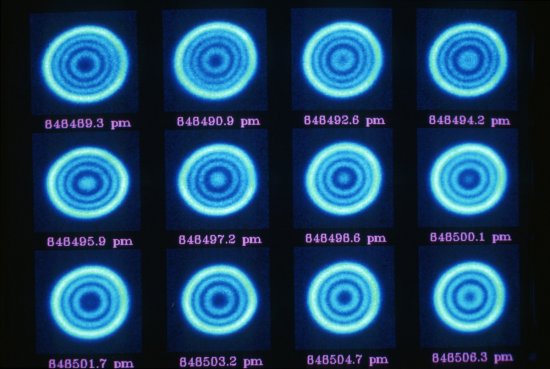
Le cristal moléculaire (au centre) dans son cryostat (appareil utilisé pour le maintenir à basse température) est irradié par un faisceau laser (en mauve). La lumière blanche, réfléchie par le cristal, est analysée par spectroscopie pour détecter le changement de phase. En deux picosecondes seulement, ce flash laser provoque un changement d'état, de la phase isolante à la phase conductrice. Application dans les mémoires moléculaires des futurs ordinateurs.
The use of media visible on the CNRS Images Platform can be granted on request. Any reproduction or representation is forbidden without prior authorization from CNRS Images (except for resources under Creative Commons license).
No modification of an image may be made without the prior consent of CNRS Images.
No use of an image for advertising purposes or distribution to a third party may be made without the prior agreement of CNRS Images.
For more information, please consult our general conditions