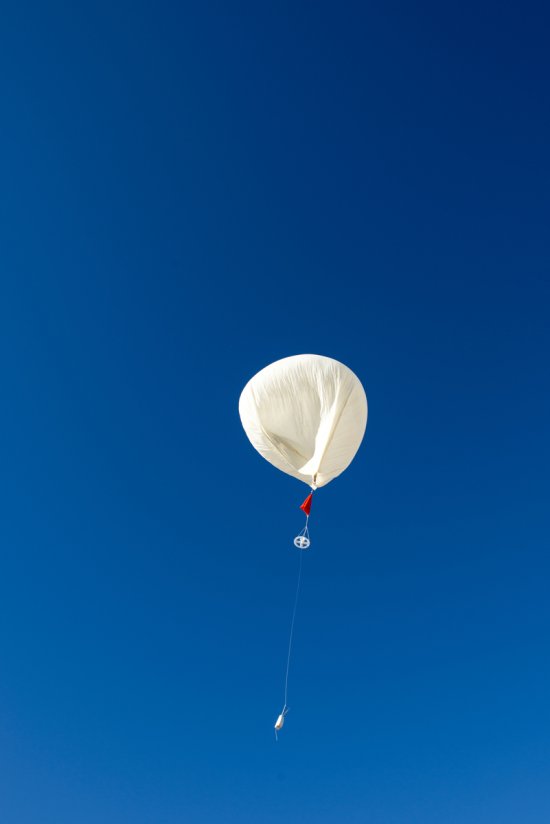
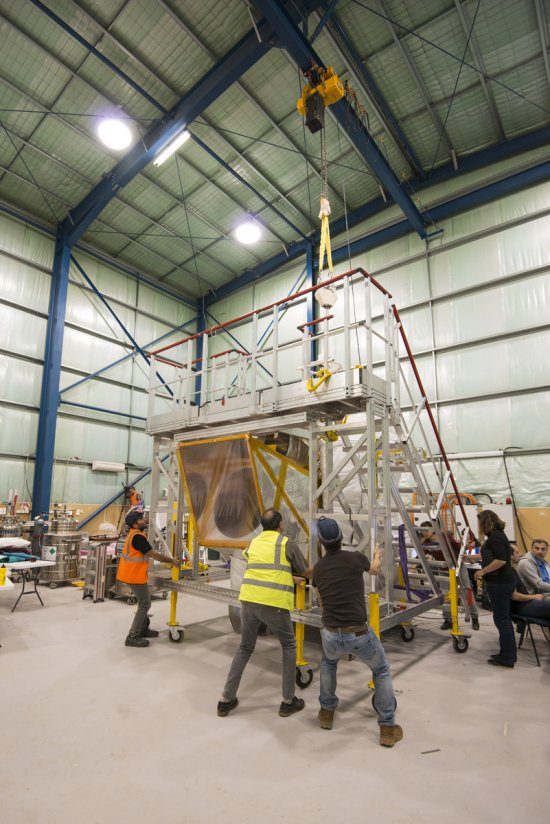
127 media
Add to my selection
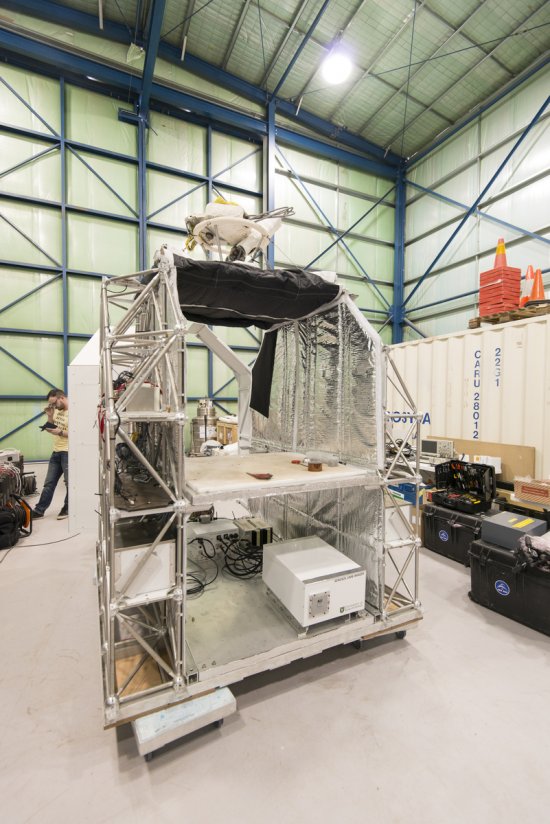
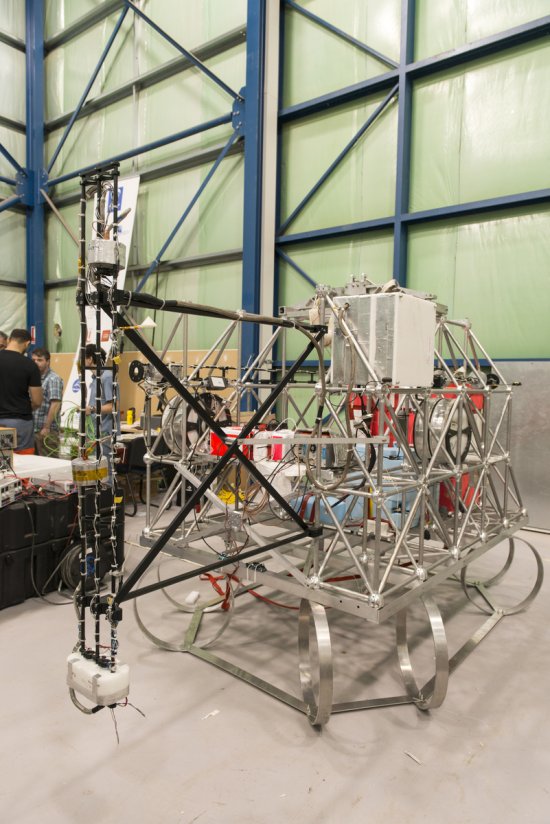
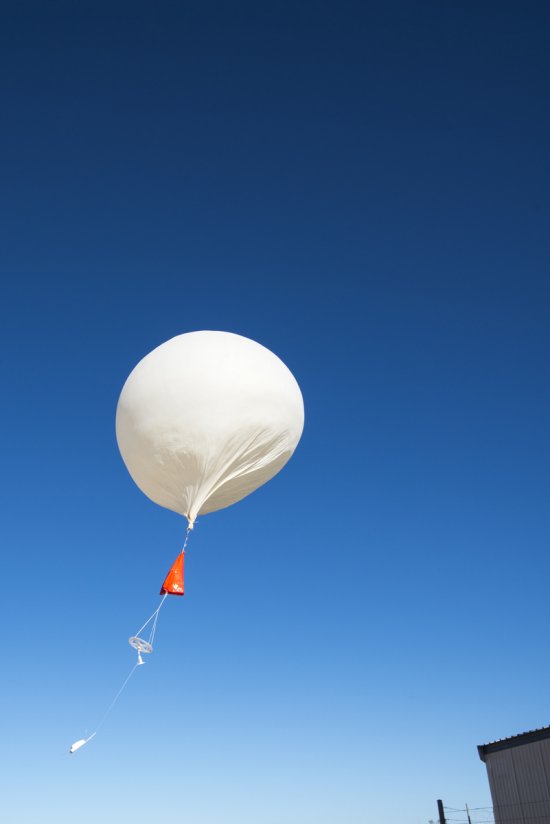
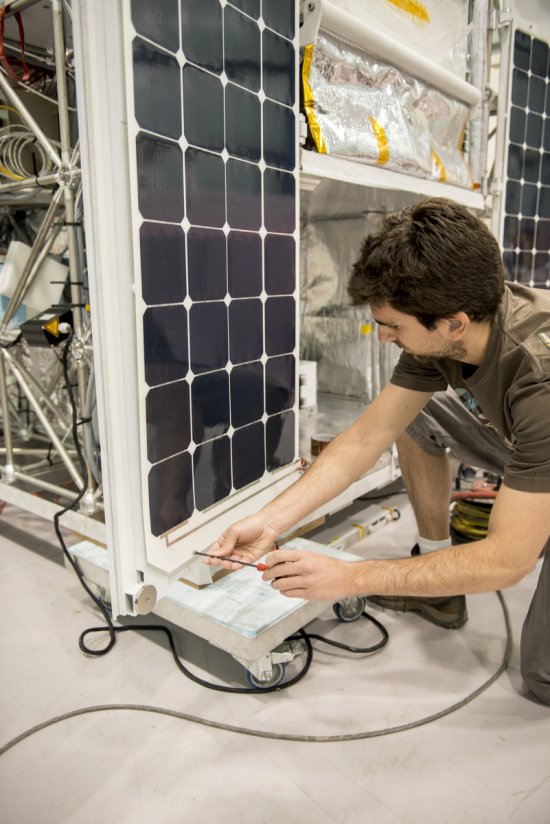
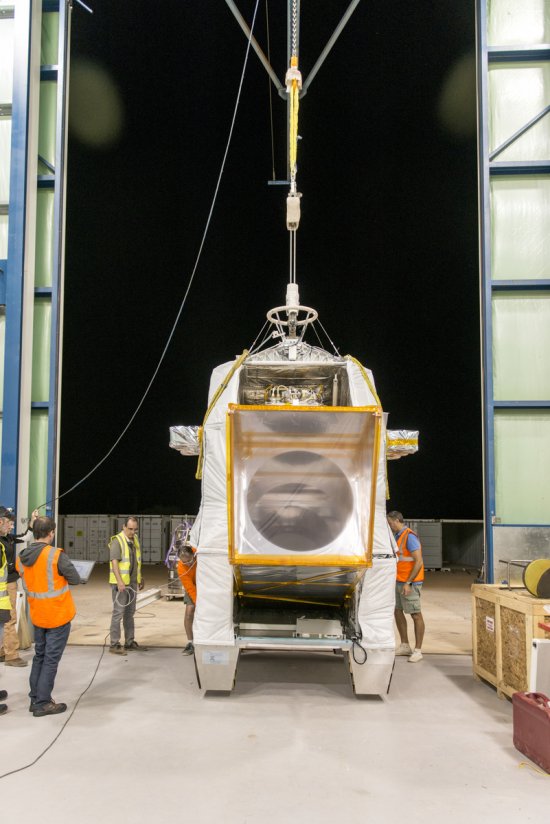
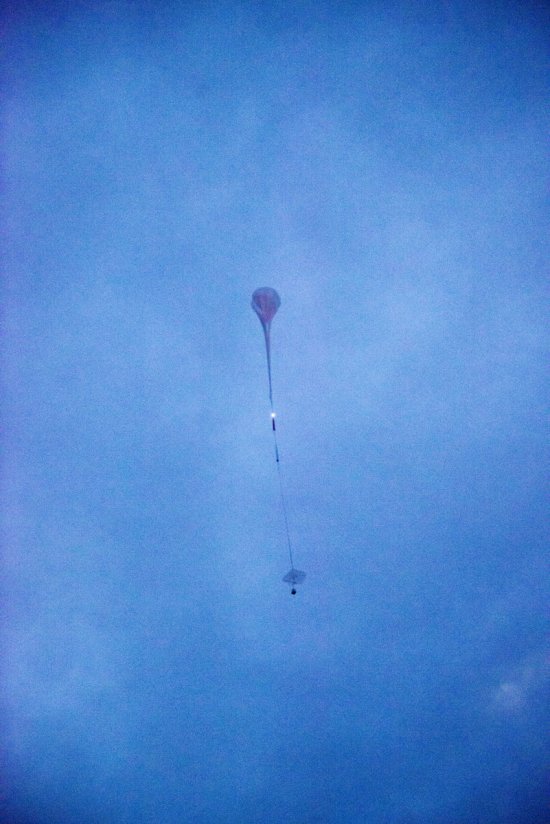
Photo
20170104_0020
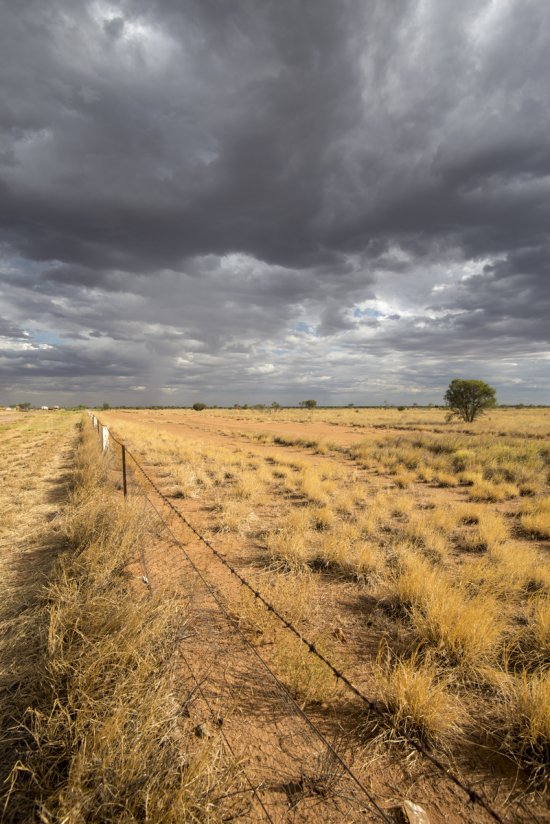
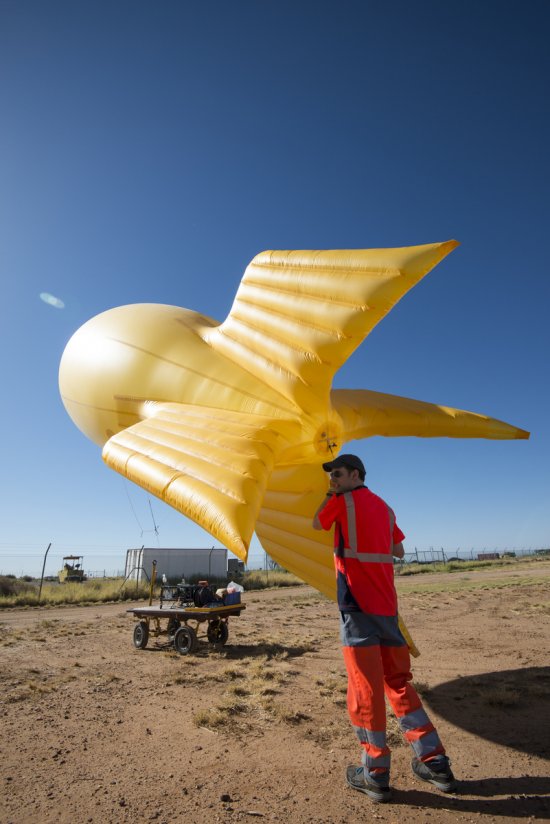
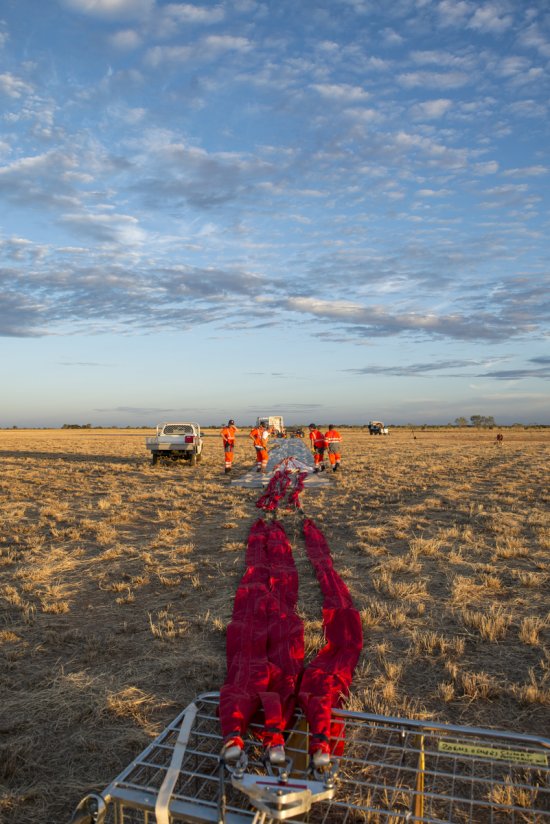
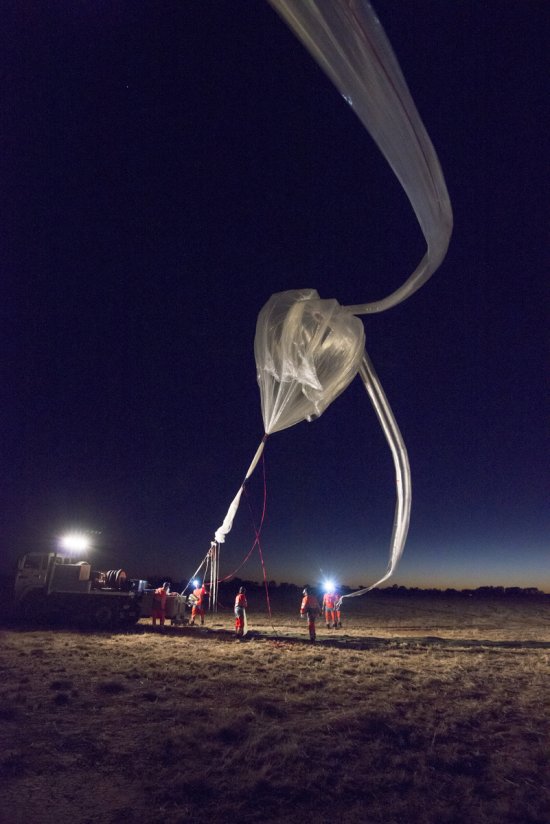
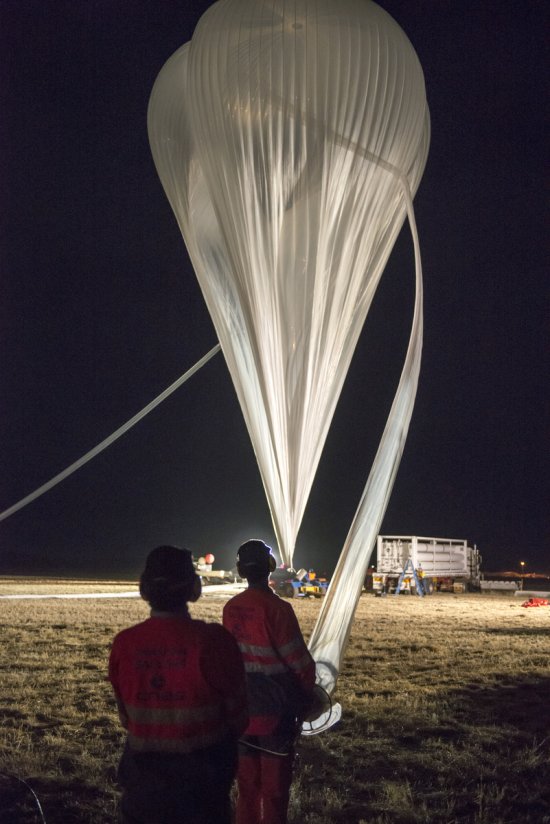
Désert environnant la base de lancement de ballons d'Alice Springs, en Australie
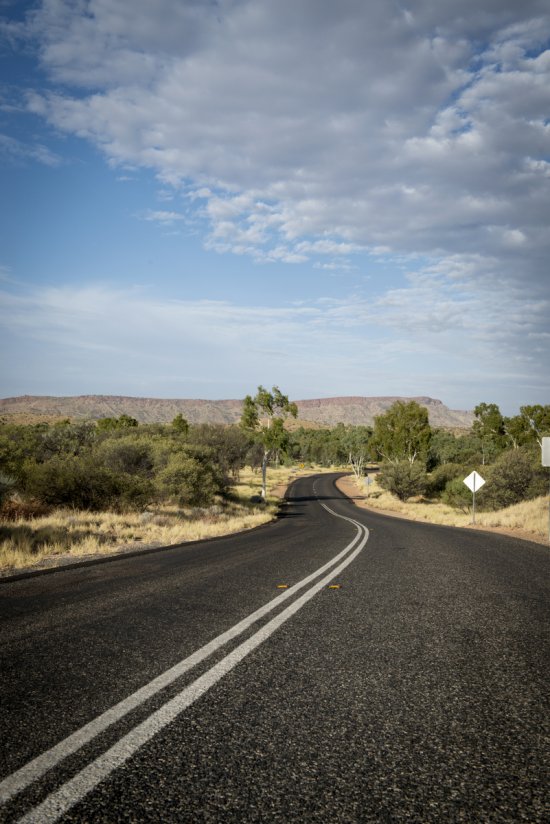
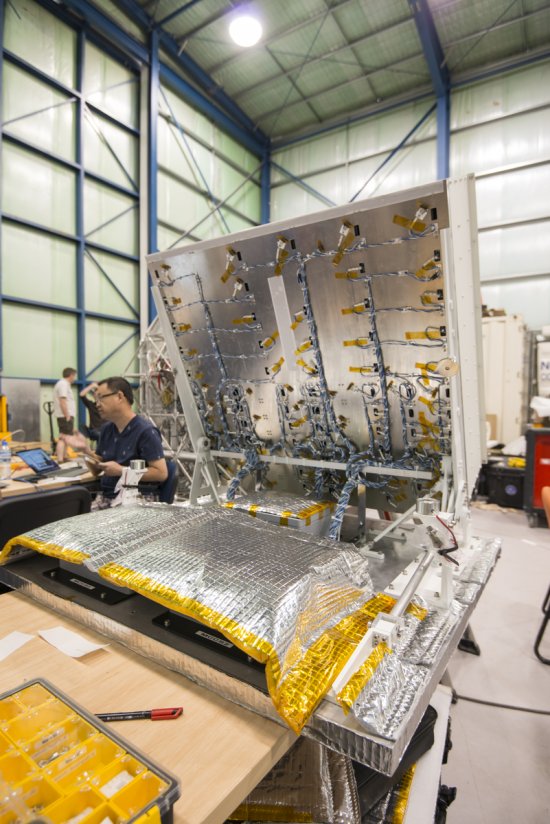
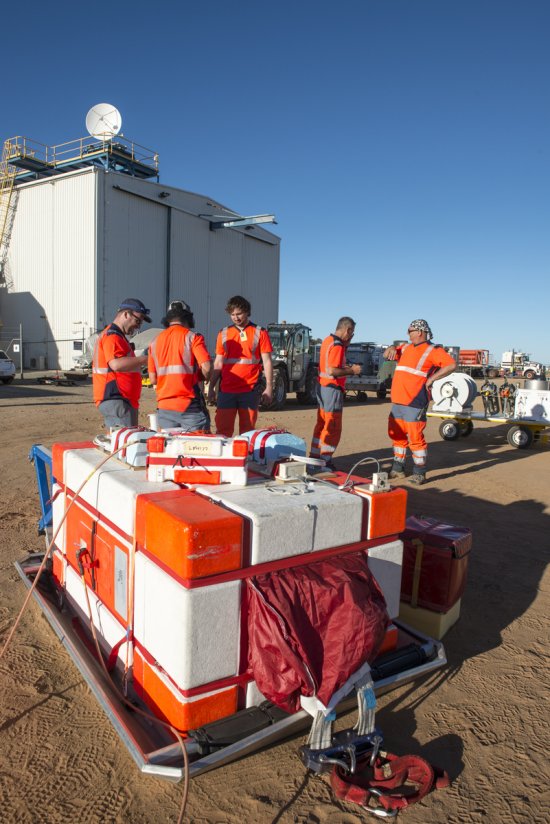
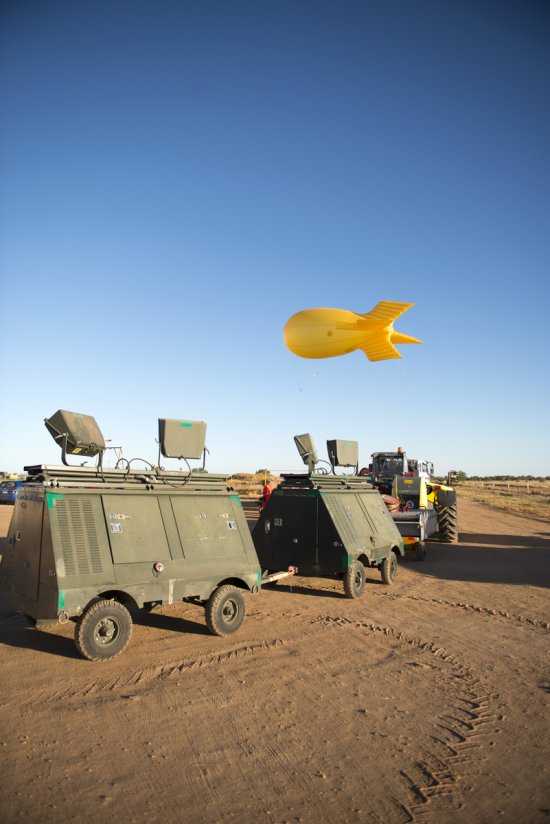
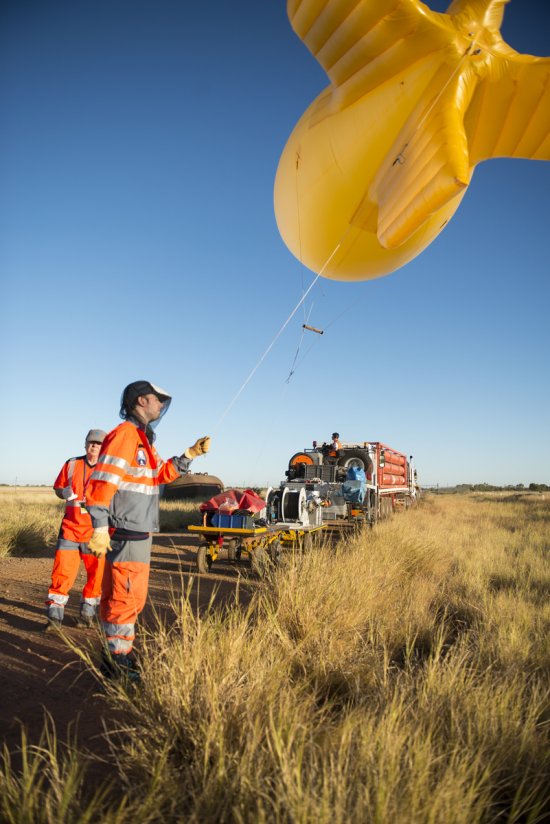
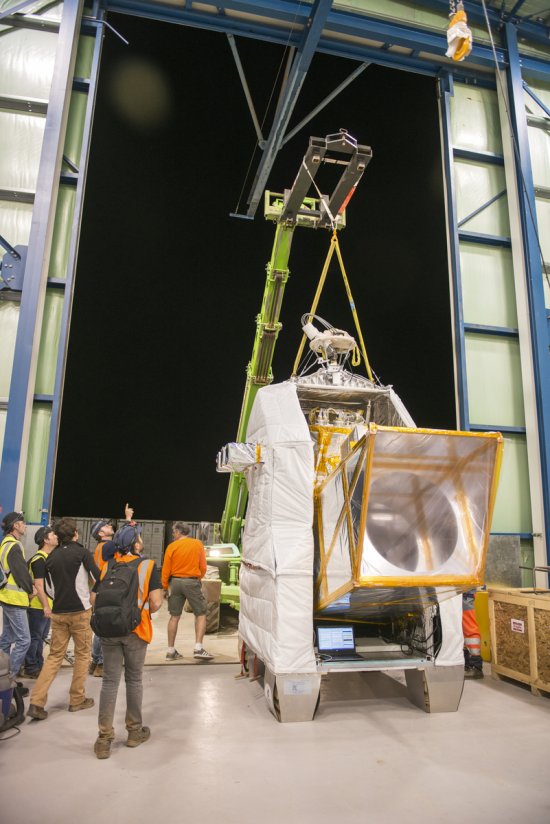
Photo
20170104_0021
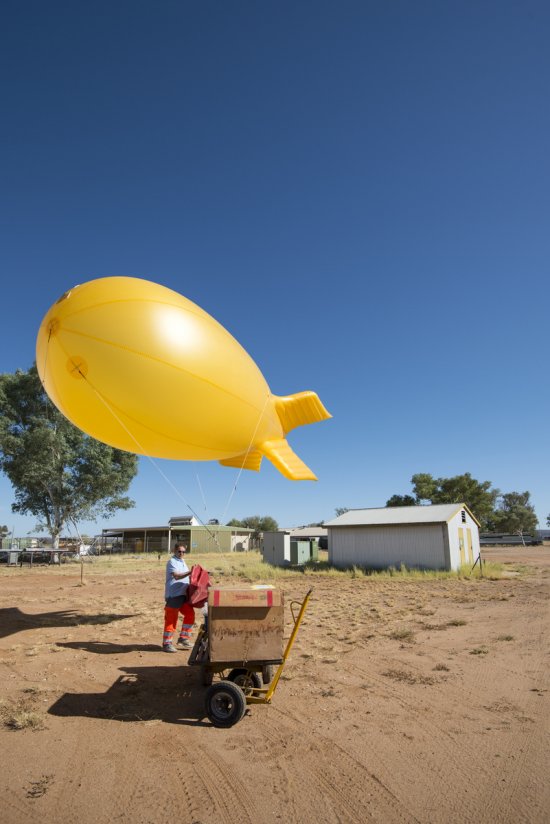
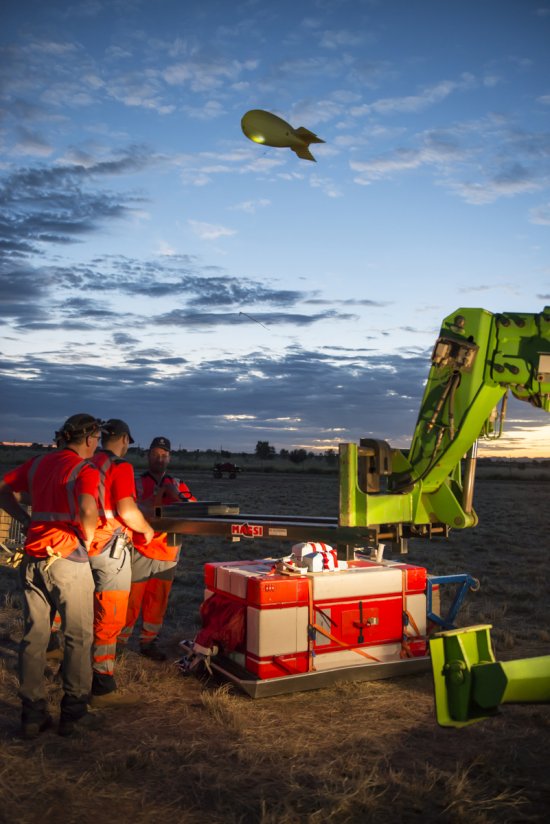
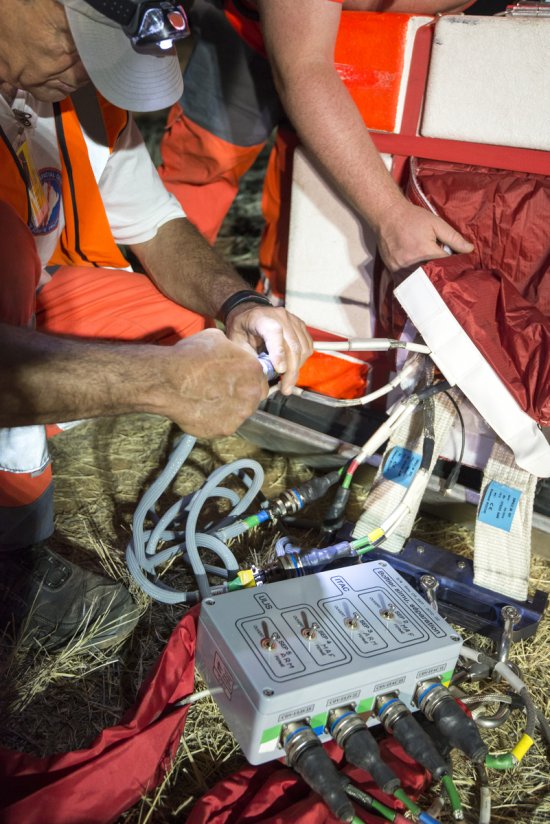
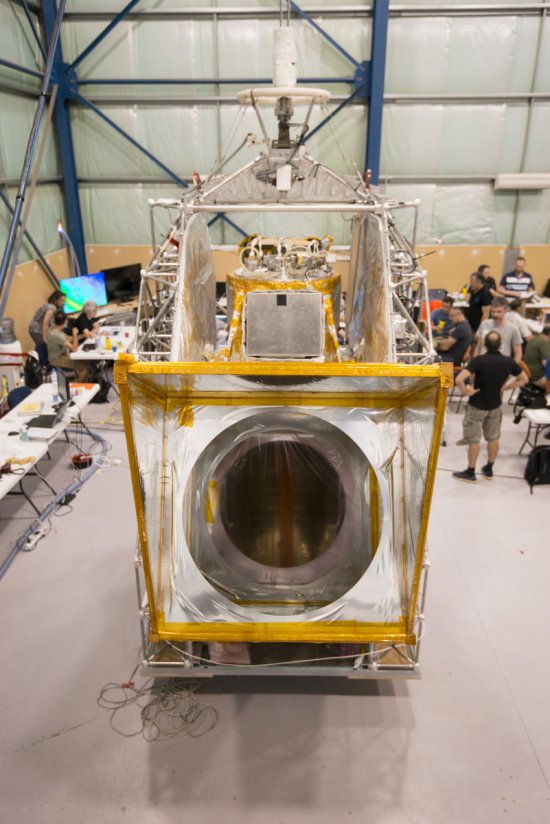
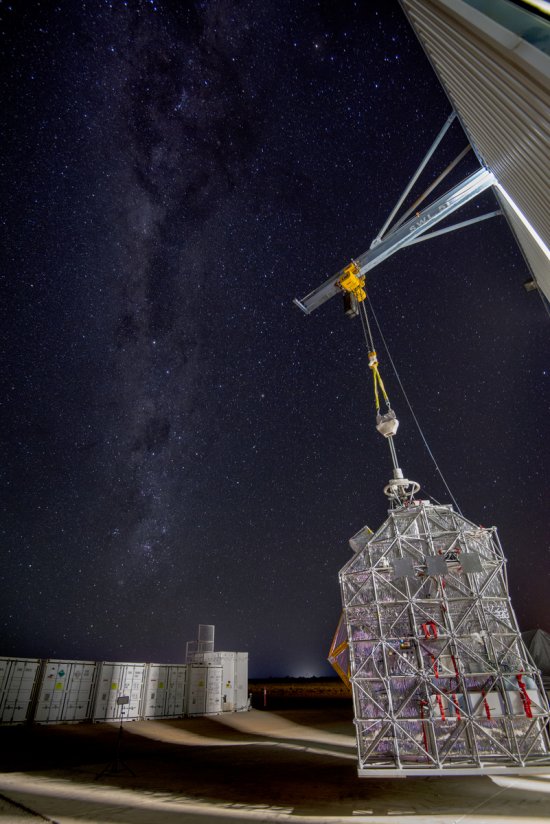
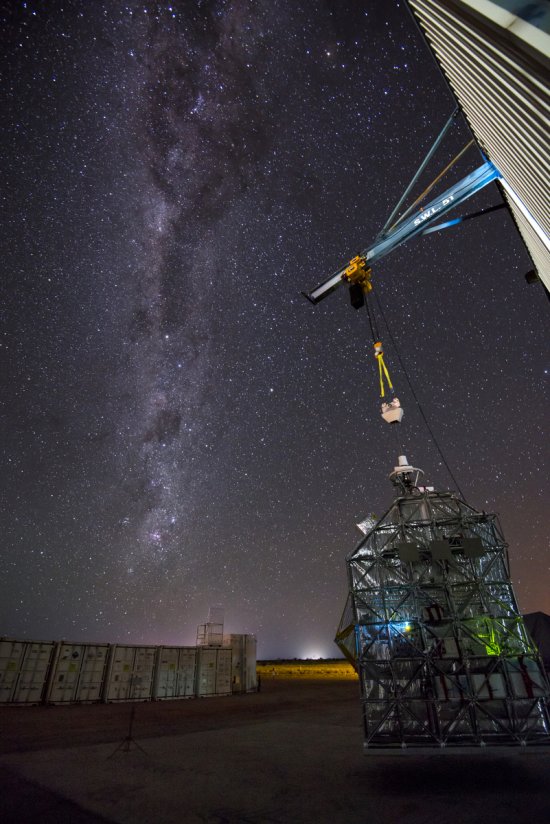
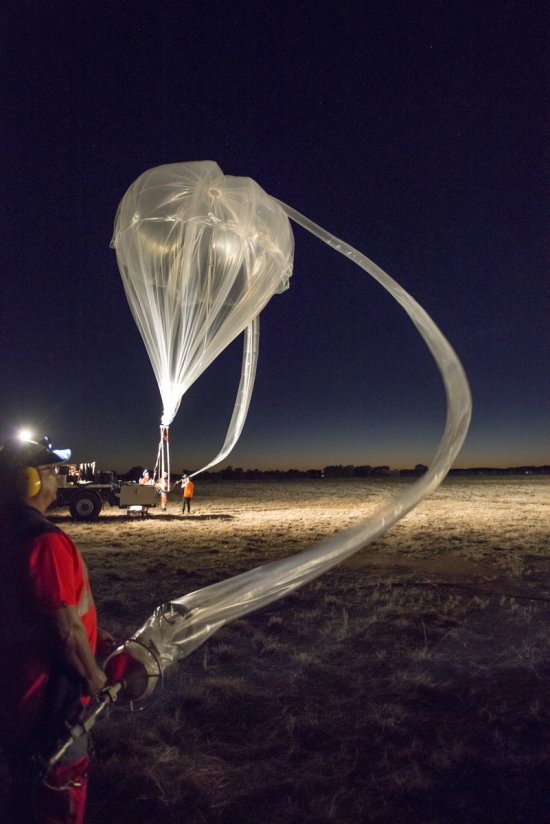
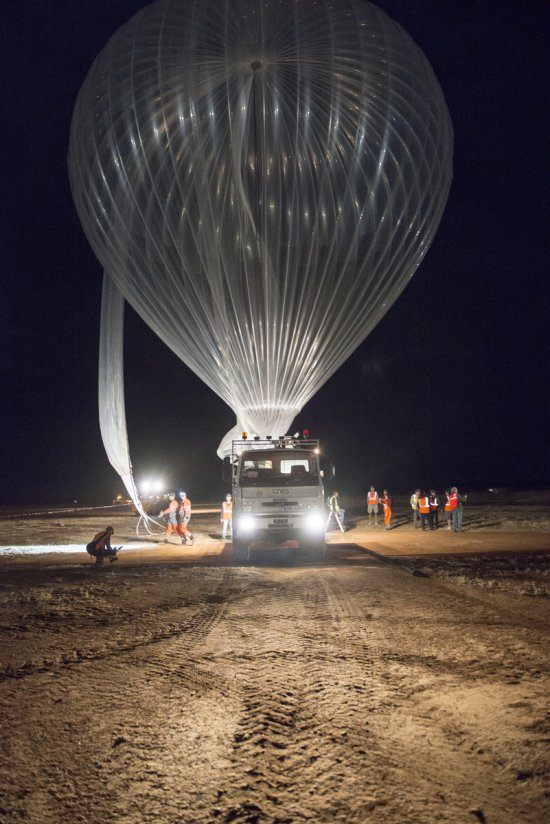
Désert environnant la base de lancement de ballons d'Alice Springs, en Australie