© Emile PEREZ/CNRS Images
Reference
20040001_0177
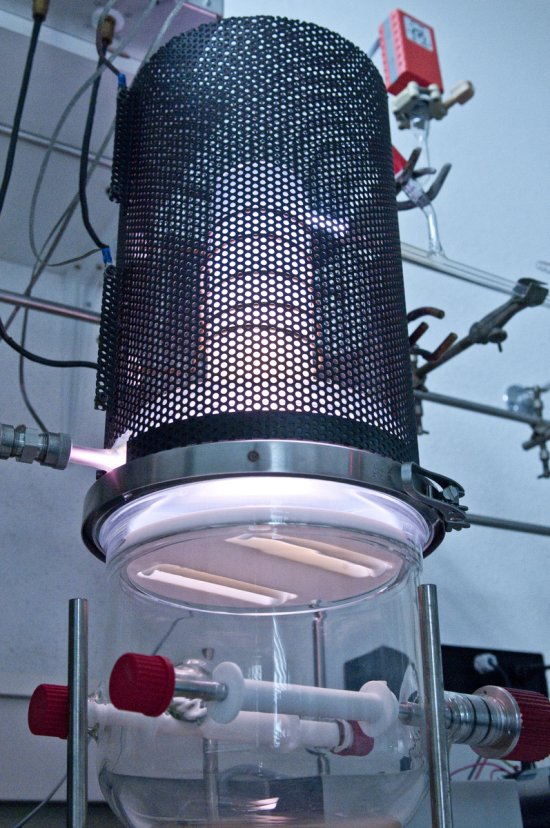
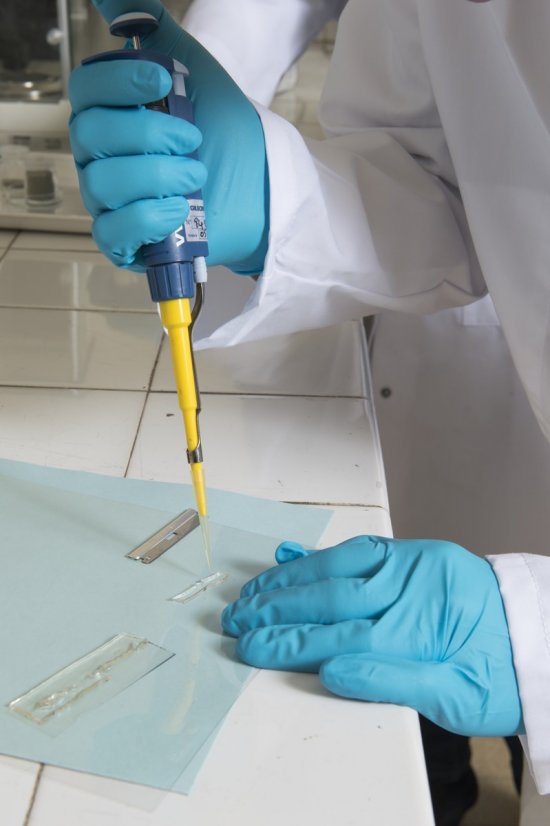
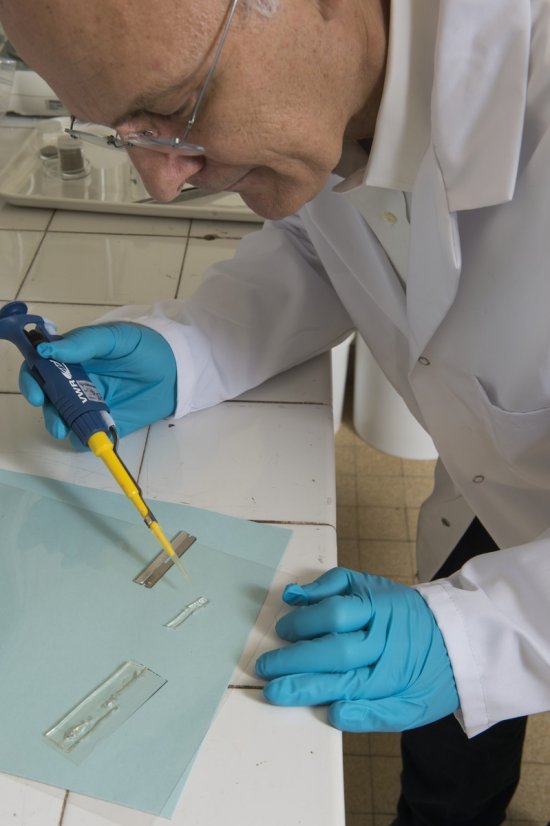
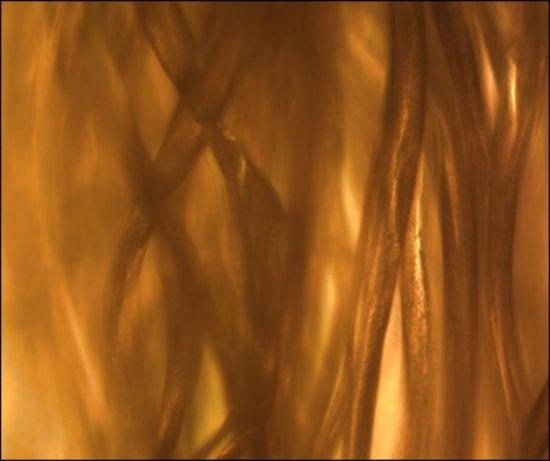
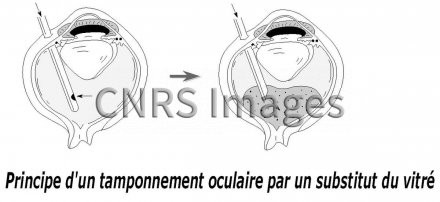
Principe d'un tamponnement oculaire par un substitut du vitré (Oxane-HD), constitué d'un fluorocarbo
Principe d'un tamponnement oculaire par un substitut du vitré (Oxane-HD), constitué d'un fluorocarbone et d'une huile de silicone (85%). L'injection de ce produit plaque la rétine contre la paroi de l'oeil et facilite ainsi les opérations chirurgicales de recollement au laser.
The use of media visible on the CNRS Images Platform can be granted on request. Any reproduction or representation is forbidden without prior authorization from CNRS Images (except for resources under Creative Commons license).
No modification of an image may be made without the prior consent of CNRS Images.
No use of an image for advertising purposes or distribution to a third party may be made without the prior agreement of CNRS Images.
For more information, please consult our general conditions